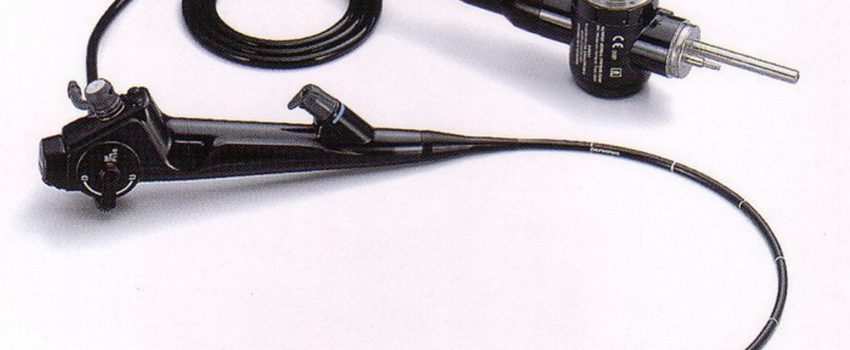
An endoscopy is a simple procedure that permits a doctor to view the insides of human bodies, using a device referred to as an endoscope. A special cutting tool maybe connected to the end of the endoscope, and this device can be used to conduct surgery (keyhole surgery).
Endoscopy involves insertion of a thin, long tube directly into the body for observing an internal organ or tissue in detail. It is useful in minor surgery and imaging. Endoscopes are minimally invasive and can be inserted into the openings of the body like anus or mouth. Additionally, they can be used also by insertion via small incisions, like in the abdomen or knee.
Modern endoscopy has much fewer risks, is carried out quickly and delivers detailed images. It has proven to be incredibly useful in many avenues of medicine. Nowadays millions of endoscopies are carried out every year.
Key Facts:
Following are key facts about endoscopy:
- It is a fast and relatively safe procedure.
- The endoscope was invented in 1806.
- The major reasons for endoscopy are treatment, confirmation and investigation.
- It can be used for removing polyps and tumours from the digestive tract.
Applications
Endoscopy is useful in a wide variety of medical situations. It is used to investigate several systems in the human body. These include:
- Gastrointestinal tract
- Respiratory tract
- Ear
- Urinary tract
- Female reproductive tract
- Incisions in the pelvic/abdominal cavity (laparoscopy), inside a joint (arthroscopy) and organs of the chest.
Capsule Endoscopy
This technique was developed in the mid-1990s and includes a wireless camera. Such a camera is small enough to fit into a capsule (size of a vitamin capsule) and can be swallowed. When the capsule passes via the digestive tract, it takes thousands of pictures that are transmitted to a device fitted on a wearable belt. It is a useful type among endoscopy equipments.
This technique of endoscopy is used to image the small intestine, a region that is tough to image using standard endoscopy. It is highly useful to examine the mucosa of the small intestine and to diagnose Crohns disease. The capsule passes via the digestive system, within 24 to 48 hours. This procedure is relatively new and provided FDA approval in the US in 2001.
Preparations
Different types of endoscopy need different preparations. The procedure does not need overnight stay in the hospital and typically takes only 1 hour. Instructions for preparations will be made by the doctor. Some common suggestions are:
- The patient may have to fast for 12 hours before the procedure.
- For procedures in the gut, it is suggested to take laxatives to clear the system.
- The doctor will carry out examinations before the endoscopy.
- Patient must inform the doctor about all current medication and previous procedures.
Reasons for Endoscopy
There are 3 main reasons for carrying out endoscopy:
- Investigation:
In case a person is suffering from abdominal pain, vomiting, stomach ulcers, breathing disorders, gastrointestinal bleeding or difficulty in swallowing, an endoscope can be used to search for the cause.
- Confirming a diagnosis
Endoscopy can be used to carry out a biopsy for confirming the diagnosis of diseases like cancer.
- Treatment
An endoscope may be used to treat an illness directly. For example, it can be used to cauterize a bleeding vessel or remove a polyp.
These are all some top facts about endoscopy.